The ProChild-2 Study
SUMMARY
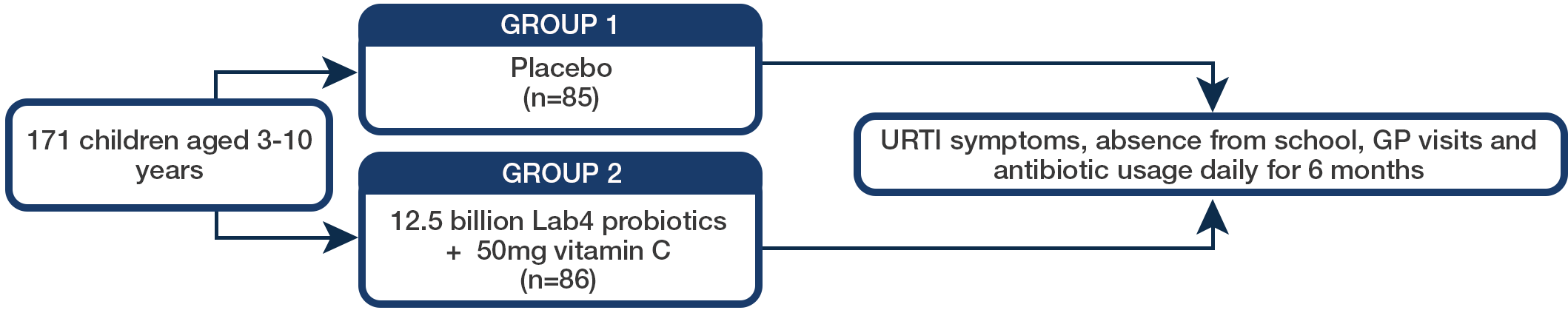
Aim
This randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled study assessed the impact of the Lab4 probiotic with low dose of vitamin C combination on the prevention of upper respiratory tract infection (URTI) symptoms and absenteeism in children aged 3 to 10 years.
Method
Results
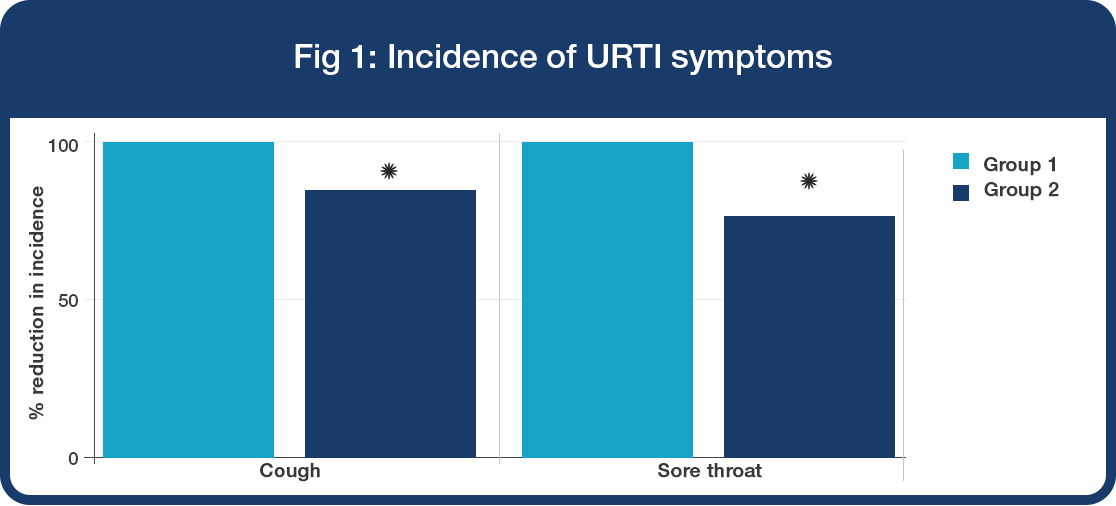
URTI symptoms
• 16% significant reduction in the incidence of coughing in Group 2 compared to Group 1 (Fig 1, *P<0.05).
• 20% significant reduction in the incidence of sore throats in Group 2 compared to Group 1 (Fig 1, *P<0.05).
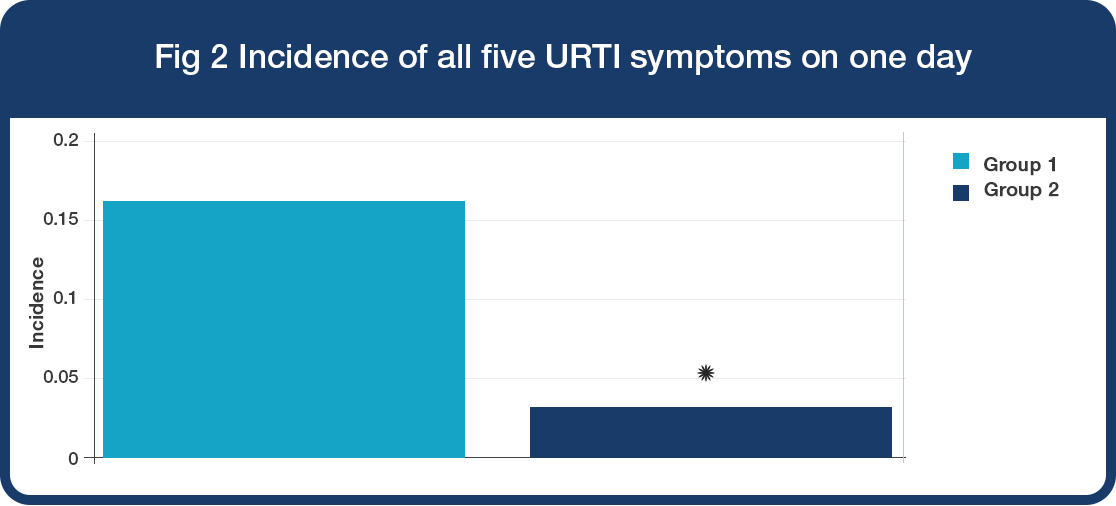
• Only 5.8% children in Group 2 had all five URTI symptoms on one day compared to 18.8% children in Group 1 (P<0.05). URTI symptoms included cough, sore throat, sneezing, runny/blocked nose.
• 79% significant reduction in the incidence of episodes with all five URTI symptoms on one day (Fig 2, *P<0.0001)
Absenteeism
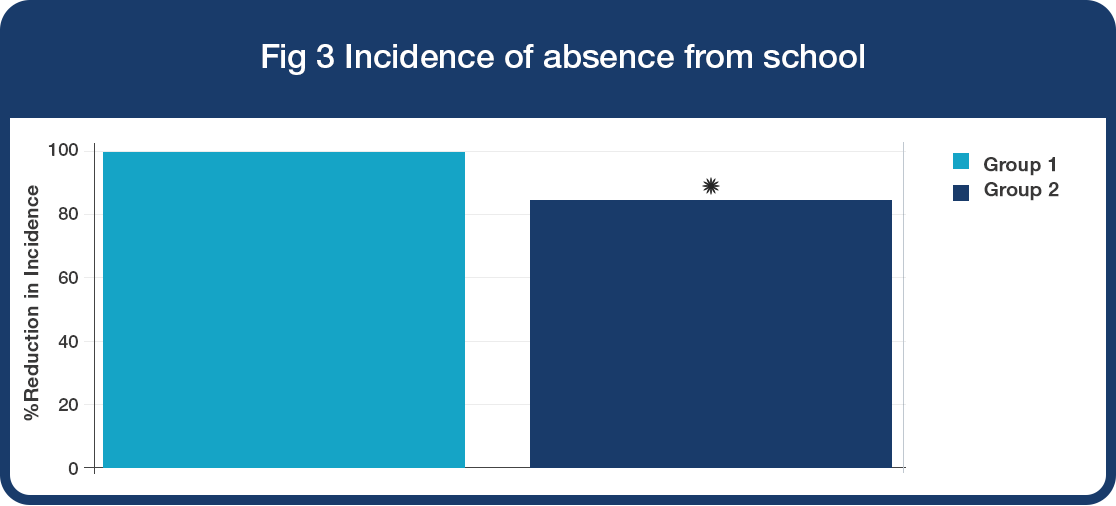
• 16% significant reduction in the incidence of absenteeism from preschool/school in Group 2 compared to Group 1 (Fig 3, *P<0.05).
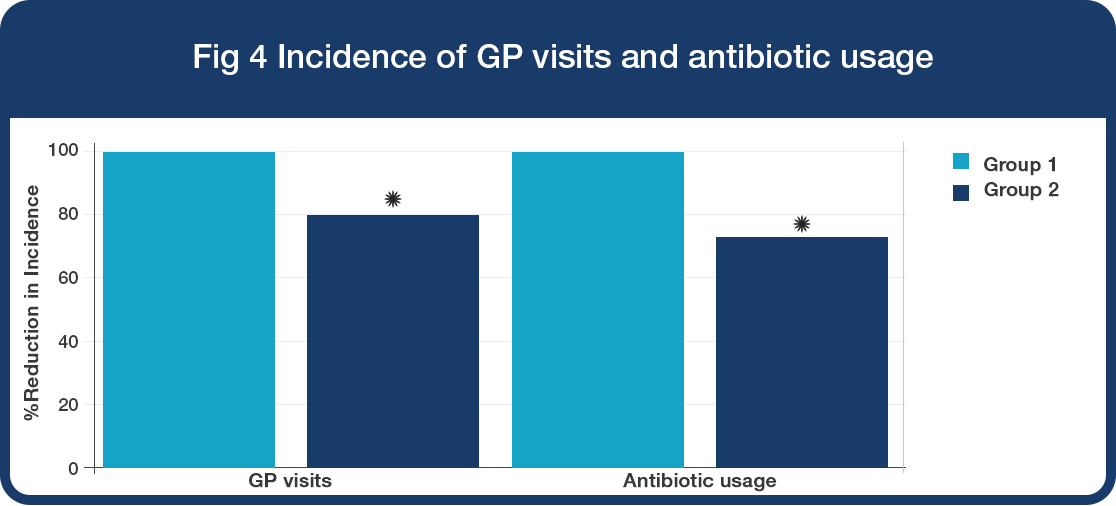
Paediatric physician’s visit and antibiotic usage
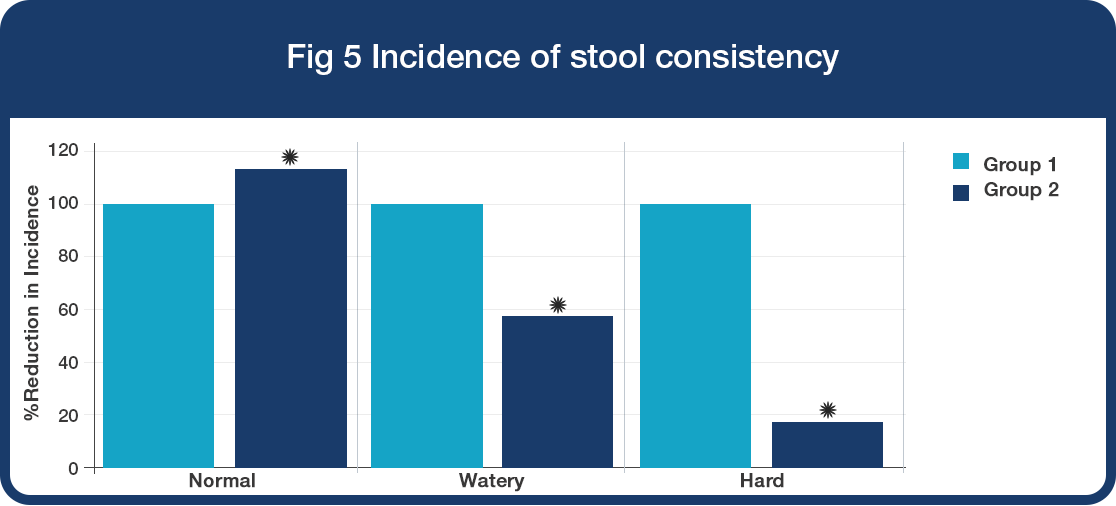
Improvement in intestinal health
Conclusion
Lab4 probiotics in combination with low dose of vitamin C reduce the incidence of coughing, sore throats together with absence from school and antibiotic use.
To our knowledge, this is the first time two probiotic studies (ProChild and ProChild-2) with the same intervention for same duration showed the beneficial effect in the management of URTIs in children attending school.

