The Cycling Endurance Study
Probiotic supplementation increases carbohydrate metabolism in trained male cyclists: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled cross-over trial
SUMMARY
The aim of this double-blind placebo-controlled crossover study was to investigate whether probiotic supplementation increases the oxidation of an ingested maltodextrin drink and total carbohydrate oxidation during 2 hours of cycling exercise at 55% maximal aerobic power output.
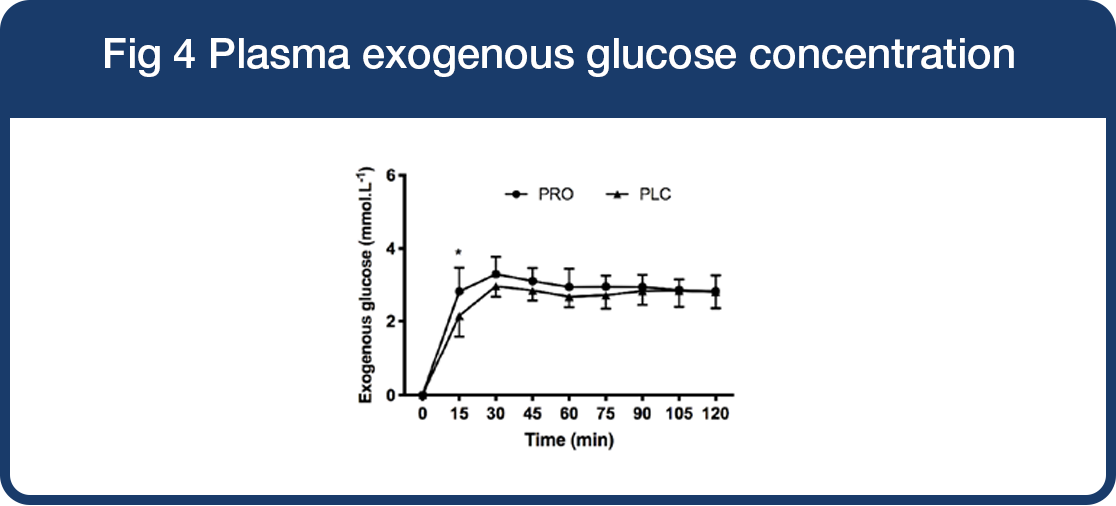
The cyclists taking Lab4 probiotics for 4 weeks were able to oxidise more of orally-ingested carbohydrates during cycling endurance exercise.
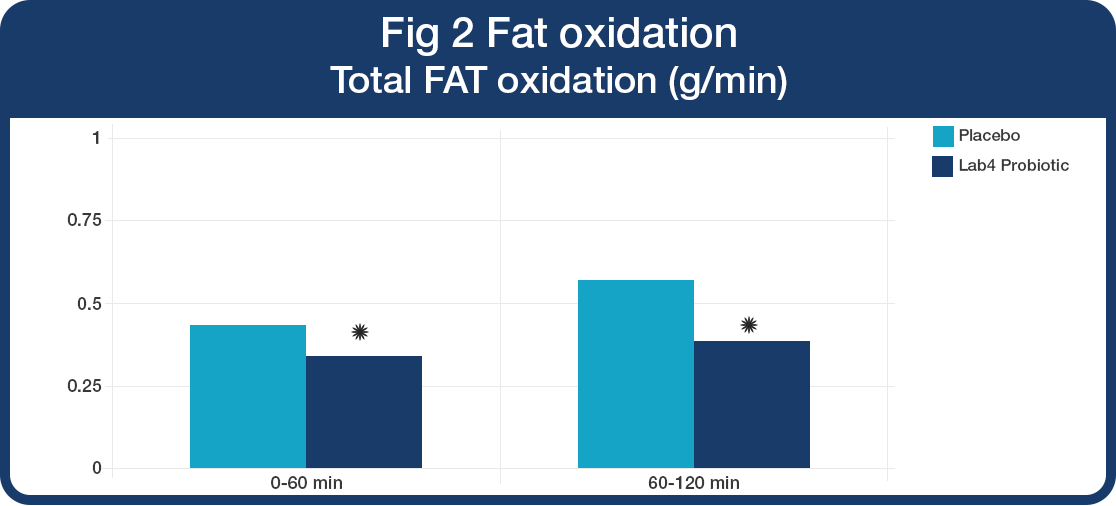
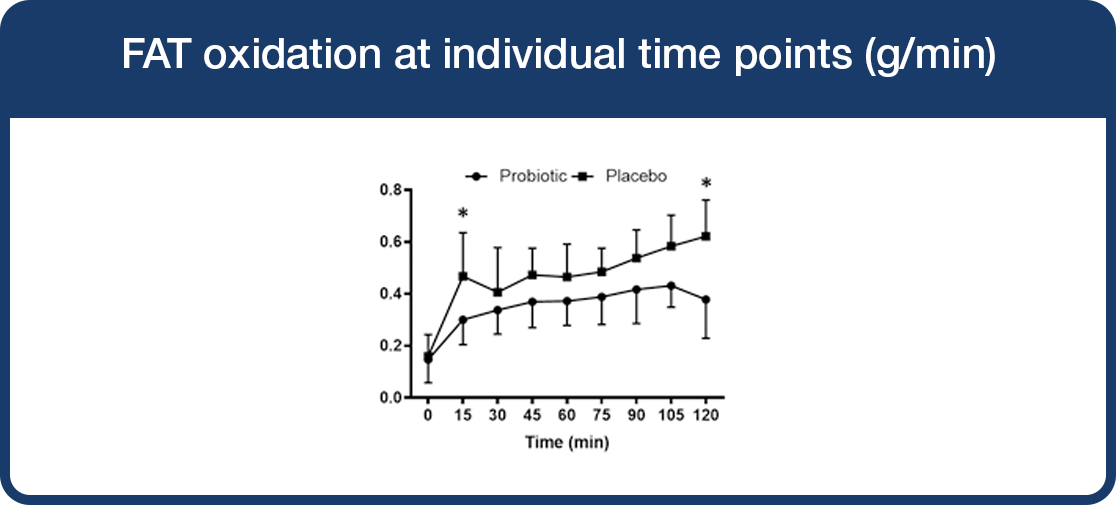
Lab4 probiotics supplementation led to a reduction in fat oxidation.
Aim
This randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled endurance study aimed to assess whether Lab4 probiotic supplementation increases the absorption and oxidation of orally-ingested maltodextrin and total carbohydrates oxidation during 2 hours’ endurance cycling.
Method
Results
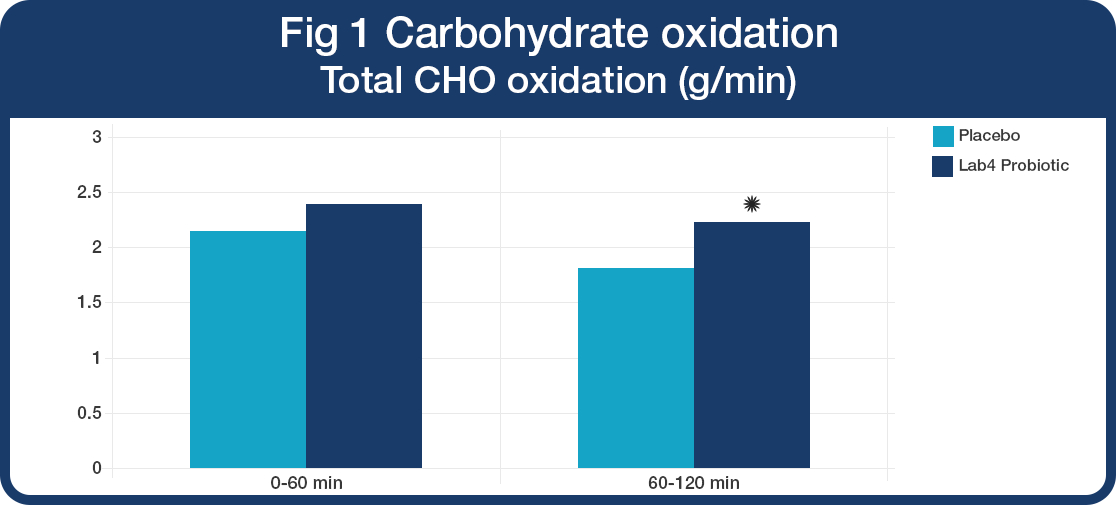
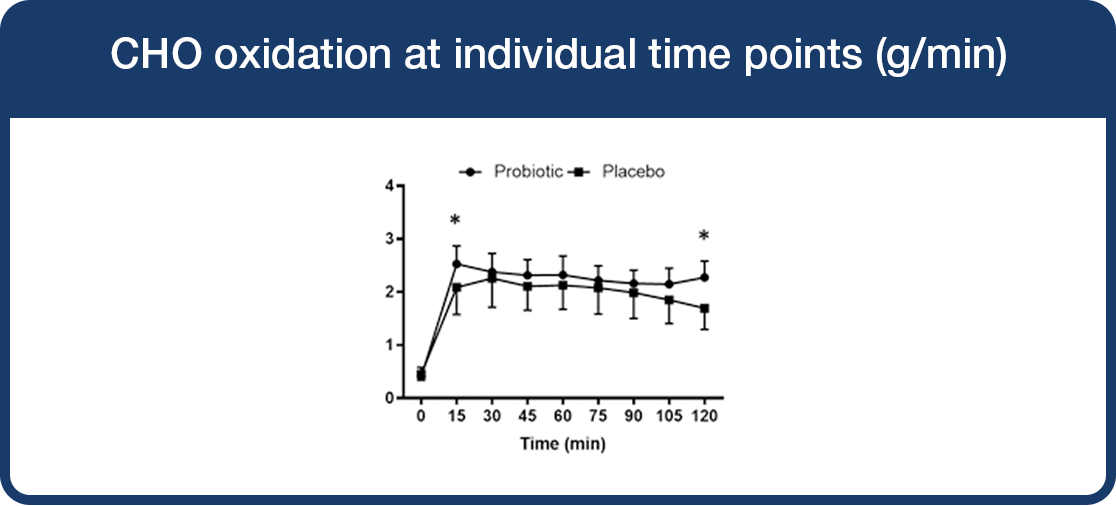
Carbohydrate oxidation
Fat oxidation
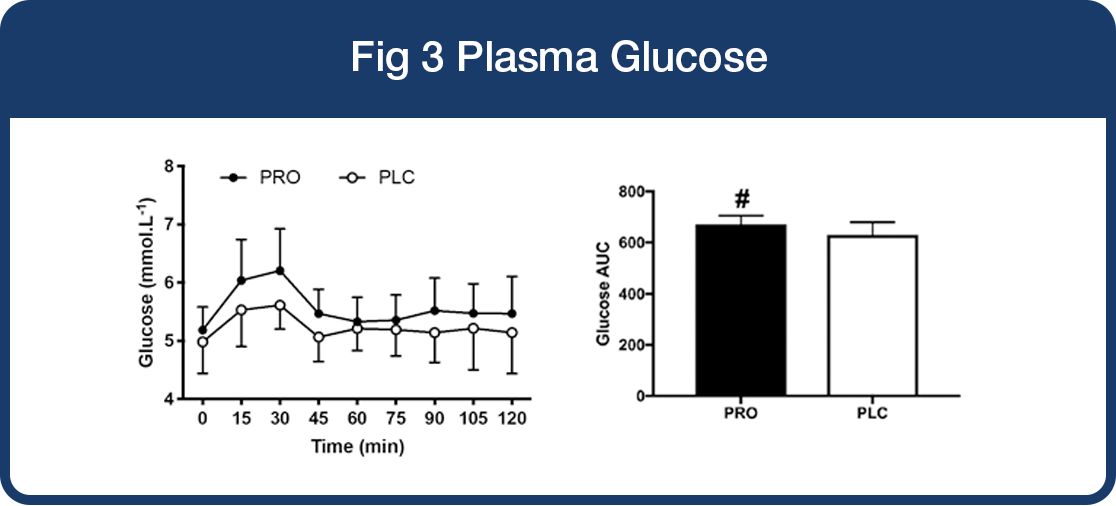
Plasma Glucose
- Significant increase in the plasma glucose levels originated from orally-ingested maltodextrin drink at 15 min of exercise in the Lab4 probiotic group compared to placebo (*P=0.01).
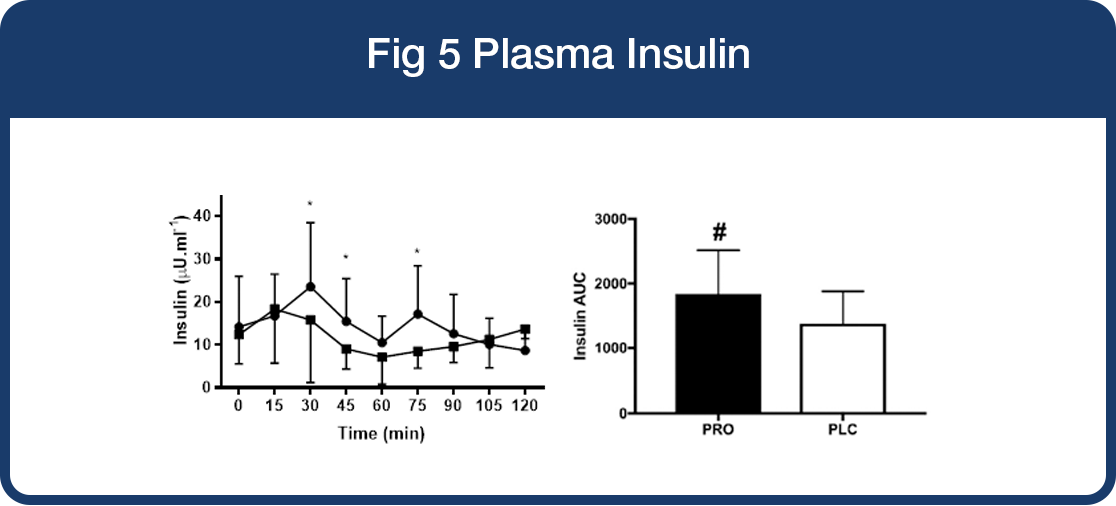
Plasma Insulin
Gut symptoms
Conclusion
Reference
Pugh JN et al 2020. Probiotic supplementation increases carbohydrate metabolism in trained male cyclists: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled crossover trial. American Journal of Physiology, Endocrinology and Metabolism 318 (4): E504-E513

