The Adult Immune Response Study
SUMMARY
This study examined the effect of daily probiotic supplementation on the immune health profile of healthy adults by assessment of ex vivo cytokine production.
Supplementation with Lab4 probiotics in combination with prebiotic fibre resulted in a significant increase in ex vivo anti-inflammatory cytokine production and a reduction in the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines (substances produced by the cells in the immune system that have an effect on other cells).
Aim
This study examined the effect of a 12-week Lab4 probiotic and fructooligosaccharide (FOS, prebiotic fibre) supplementation on ex vivo pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory cytokine production by peripheral blood mononuclear cells extracted from healthy volunteers.
Method
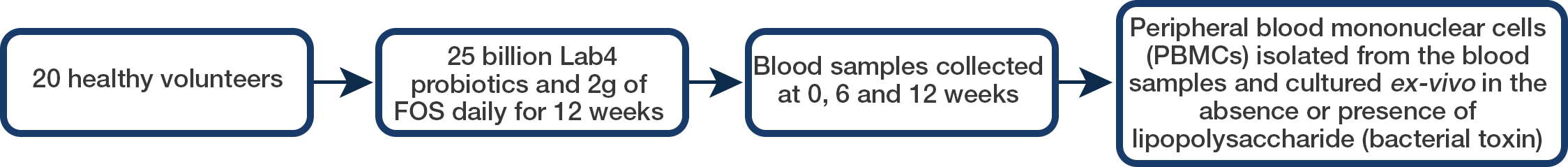
Results
In the ‘resting’ immune state:
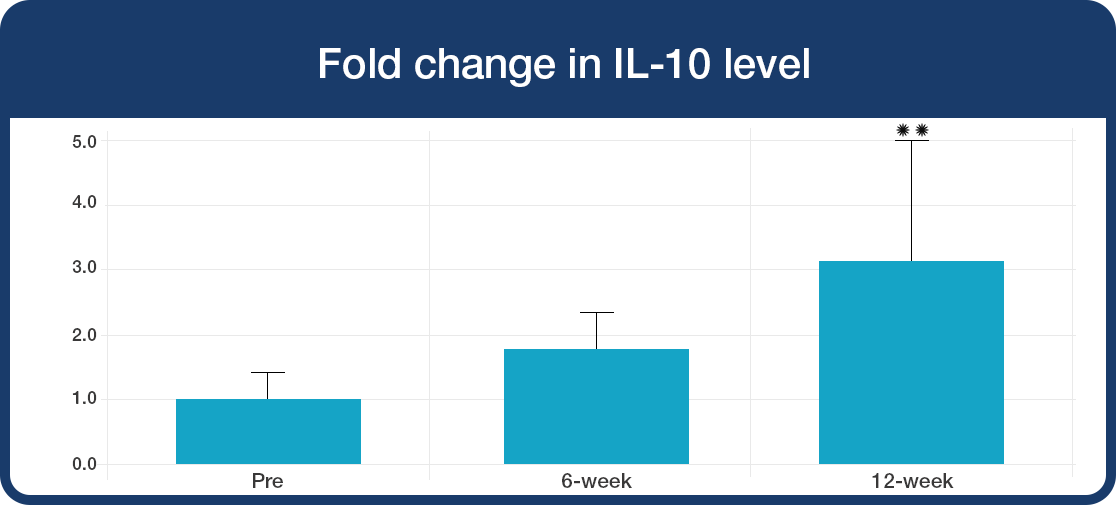
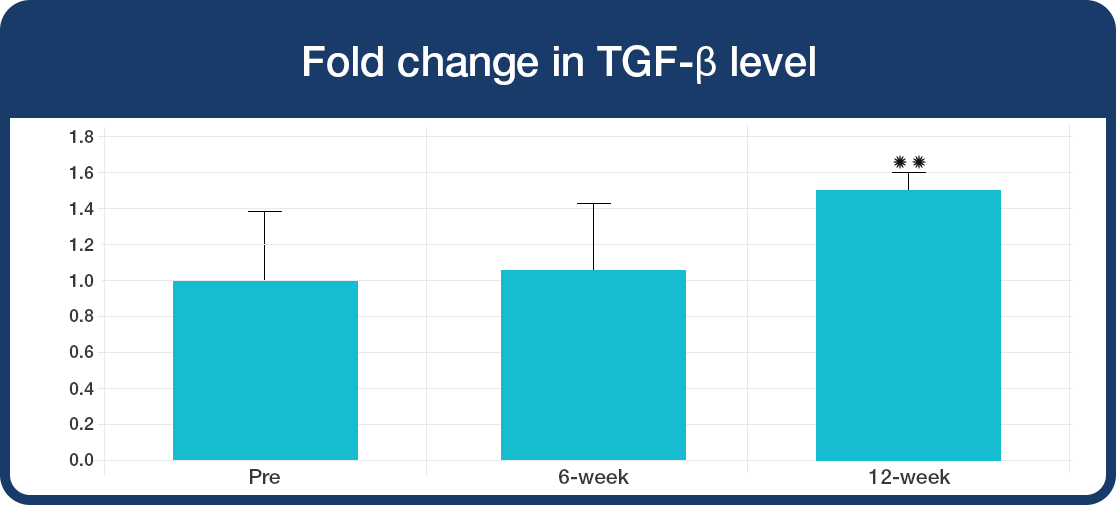
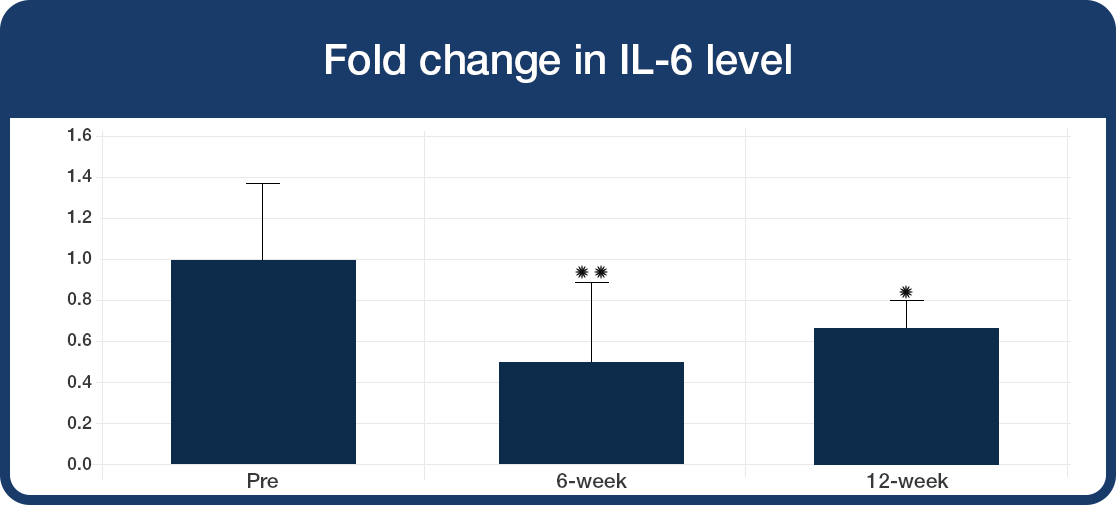
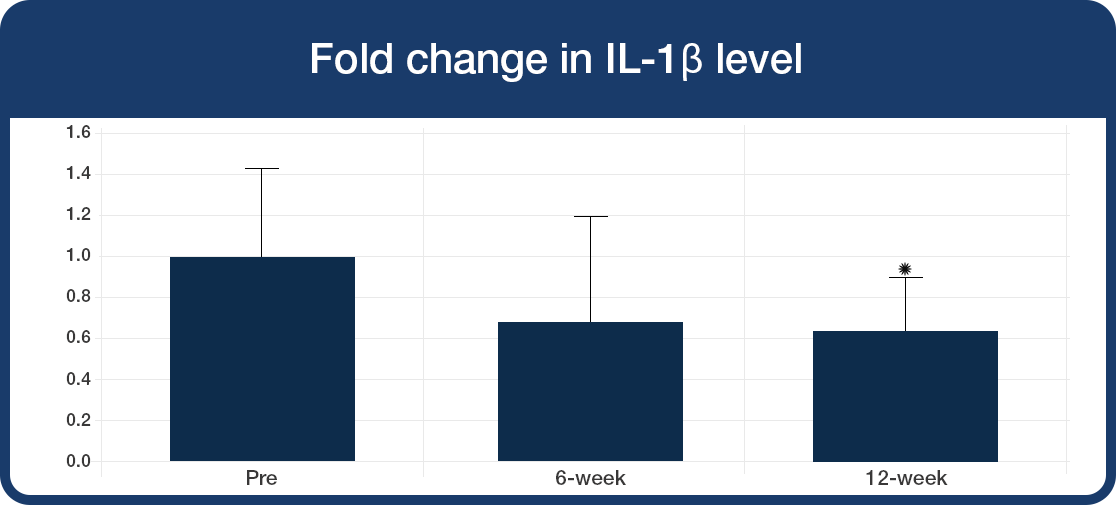
During challenge with bacterial toxin:
- Significant decrease in production of the pro-inflammatory cytokines IL-6 and IL-1β (*P<0.01,**P<0.0001)
Conclusion
The consumption of Lab4 probiotics in combination with FOS alters ex vivo cytokine production demonstrating the potential immunomodulatory benefits.

